GPIOs on Astra Machina
Astra Machina integrates many GPIOs to support its various functionalities. This guide will cover how to use GPIOs with Astra Machina and configure their functionality.
On Astra Machina:
All of the GPIOs are multiplexed and can be configured for different functionality.
All GPIOs can be assigned interrupts. However, GPO (output only pins) cannot.
Specific details on GPIOs can be found in the Astra Machina Eval Platform.
Accessing GPIOs from Userspace
GPIOs can be accessed and configured using the GPIO sysfs interface /sys/class/gpio. GPIOs can be exported to userspace and their
direction and value can be viewed or set.
For example, to export GPIO[36] on SL1680 run the command:
root@sl1680:~# echo 484 > /sys/class/gpio/export
GPIO[36] is located on the 40 pin connectors on SL1640 and SL1680. GPIO[36] maps to GPIO number 484 based on the instruction in GPIO Mappings.
Once the GPIO has been exported, the value and direction can be viewed and set:
root@sl1680:~# cd /sys/class/gpio/
root@sl1680:/sys/class/gpio/gpio484# cat direction
in
root@sl1680:/sys/class/gpio/gpio484# cat value
0
By default, GPIO[36] is set to input with the value 0. To changes these value, write to the corresponding sysfs file:
root@sl1680:/sys/class/gpio/gpio484# echo "out" > direction
root@sl1680:/sys/class/gpio/gpio484# cat direction
out
root@sl1680:/sys/class/gpio/gpio484# echo 1 > value
root@sl1680:/sys/class/gpio/gpio484# cat value
1
Changing the Function of GPIOs
GPIOs which are assigned to other functionality can be reconfigured to function as generic GPIOs. This is done by updating
the device tree entries in the Linux Kernel. This requires modifying the linux-syna package using devtool:
devtool modify linux-syna
Modify the platform dts file located in build-sl1680/workspace/sources/linux-syna/arch/arm64/boot/dts/synaptics.
SL1620 |
SL1640 |
SL1680 |
|
DTS |
myna2-rdk.dts |
platypus-rdk.dts |
dolphin-rdk.dts |
First, identify where the GPIOs are currently configured in the dts file and disable them. Then reassign them to function as GPIOs.
The following example will reassign GPIO[12] and GPIO[13] to function as GPIOs in SL1620.
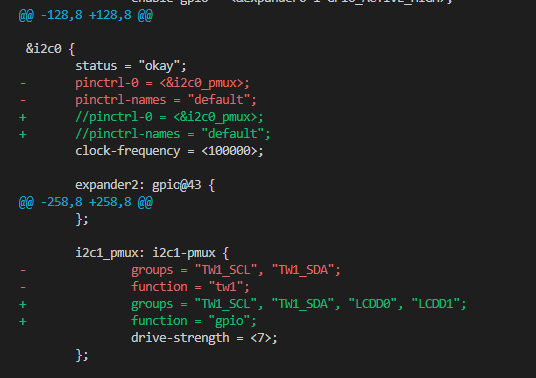
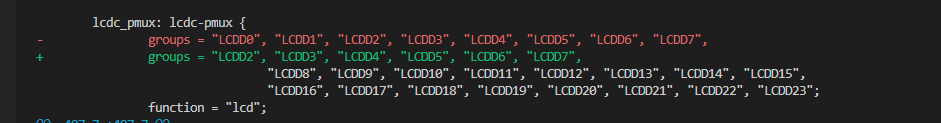
Build the image with the updated device tree entries:
devtool build linux-syna
devtool build-image astra-media
GPIO Mappings
Userspace GPIO IDs are assigned based on the gpiochip number which is assigned dynamically. Changes in the device configuration, such as updating the device tree (DTS), can cause the gpiochip number to change. Therefore, userspace GPIO IDs need to be calculated using the current gpiochip number assigned to the GPIO port.
GPIOs 0 - 31:
GPIOs 32 - 63:
GPIOs 64 - 95:
To do this calculation start by identifying the gpiochip number for the controller on which the GPIO is attached. The address will match
the GPIO ports in the tables below. Find which gpiochip is associated with which GPIO port by running ls -l /sys/class/gpio. The symlink
will contain the GPIO port address of the port associated with the gpiochip.
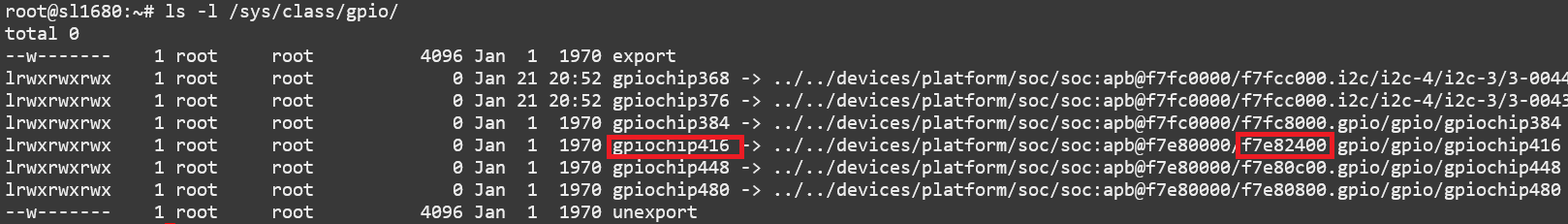
gpiochip numbers on SL1680
The following examples show how to calculate GPIO IDs for various GPIOs. Using the gpiochip number associated with the GPIO port.
Calculate GPIO[5]:
Calculate GPIO[46]:
Calculate GPIO[80]:
SL1620
GPIO Port |
Address |
GPIOs |
|---|---|---|
gpio0: gpio@0800 |
f7e80800 |
0 to 31 |
gpio1: gpio@0c00 |
f7e80c00 |
32 to 63 |
gpio2: gpio@1000 |
f7e81000 |
64 to 95 |
SL1640 / SL1680
GPIO Port |
Address |
GPIOs |
|---|---|---|
gpio0: gpio@2400 |
f7e82400 |
0 to 31 |
gpio1: gpio@0800 |
f7e80800 |
32 to 63 |
gpio2: gpio@0c00 |
f7e80c00 |
64 to 95 |